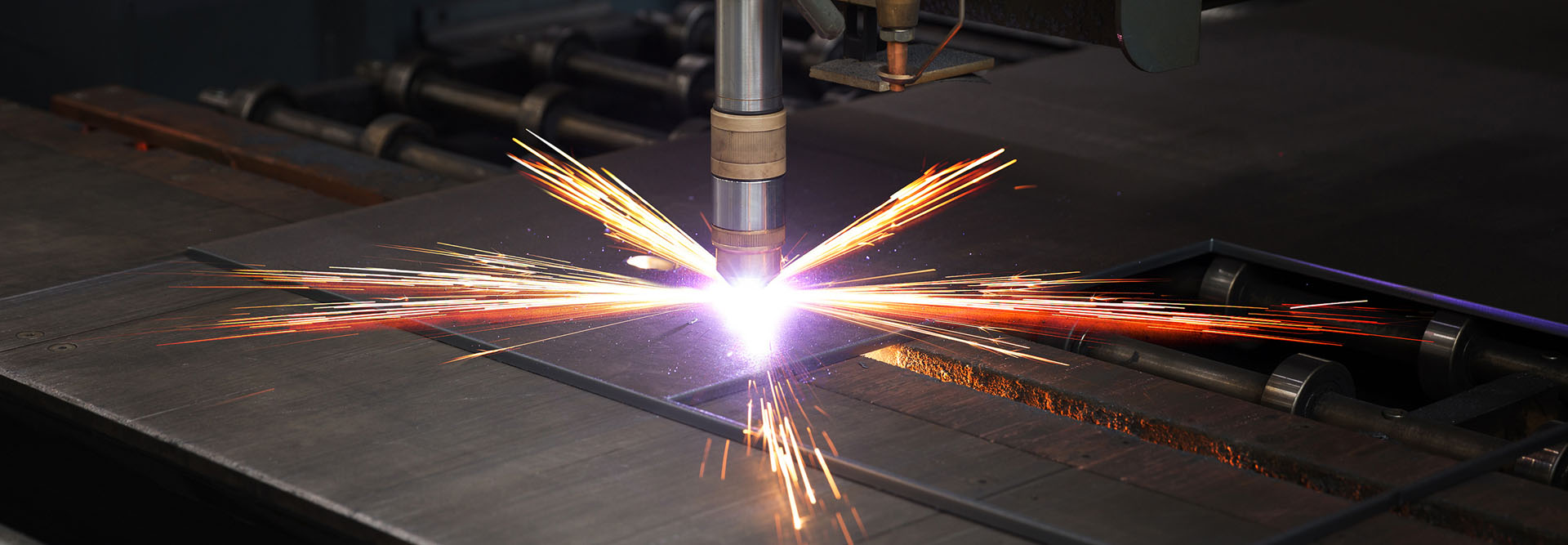
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a focused stream of ionized gas, or plasma, to cut through sheet metal. The plasma is generated by heating a gas, such as air, to extremely high temperatures, creating a plasma stream that is directed towards the cutting location by a nozzle. When the plasma contacts the surface of the metal, it melts the metal into a molten state, and the position of the plasma stream is precisely controlled to follow the desired cutting path. This process is highly efficient, allowing for quick, accurate cuts on a wide range of metal thicknesses, and it is widely used in the manufacturing and fabrication industry for cutting sheet metal, steel, aluminum and other conductive materials.
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a high-speed stream of ionized gas, or plasma, to cut through metal. The plasma is created by heating a gas, such as air or argon, to extremely high temperatures, creating a plasma stream that is directed towards the cutting location by a nozzle. The plasma stream is focused by a constricting orifice, increasing its temperature and velocity, and making it capable of cutting through metal. When the plasma contacts the surface of the metal, it melts the metal into a molten state, and the position of the plasma stream is precisely controlled to follow the desired cutting path.
The plasma cutting process has several advantages over other cutting methods such as oxy-fuel cutting. It can cut materials up to 5 times faster, with less heat-affected zone and less distortion, it can also cut a wider range of thicknesses and materials. Plasma cutting is widely used in many industries such as metal fabrication, automotive, shipbuilding, aerospace and many more.
Plasma cutting can be done using hand-held plasma cutting torch, or CNC plasma cutting machines, which are computer-controlled cutting machines that can cut metal with high precision and accuracy.
The plasma cutting process requires a power source, a plasma torch, a gas supply, and a water table or other means of collecting the molten metal and slag. Many different gases can be used for plasma cutting, including air, nitrogen, and argon. The choice of gas depends on the metal being cut, the thickness of the metal, and the desired cut quality.